Plastic Cast Film Industry
Extensive material range & market reach
The cast film process involves the extrusion of polymers melted through a slot or flat die to form a thin, molten film. We typically speak of a film when its thickness is below 1 mm. Thicker materials (> 1 mm) are sheets. These thin plastic membranes are used to separate areas or volumes, to hold items, to act as barriers, or as printable surfaces. As most plastics can be formed into a thin film, the non-exhaustible materials list covers PE, PP, Polyester (e.g. BoPET), Nylon, Polyvinyl chloride, PVC, Polycarbonate and PLA as well as a variety of bioplastics and biodegradable plastics. The use of coextrusion is on the rise, simultaneously extruding multiple materials from a single die to form a multi-layered film. This responds to the need for plastic films offering a performance that cannot be achieved by films composed of a single material.
With rising global population and disposable income, plastic films are finding increasing applications in packaging as well as in non-packaging sectors globally. In packaging, plastic films are used in food, pharmaceuticals, personal care, industrial and other applications. Today, plastic films are extensively used in flexible packaging. In non-packaging, plastic films find applications in agriculture, construction, medical and health care, consumer goods, and others.
Asia-pacific is the key market for plastic films with more than 30% of global market share, fuelled by the rising middle class in China and India. North America and Europe are experiencing slow growth in the sector, with specialty films and biodegradable films slowly gaining importance.
Maintain consistent thickness in cross machine direction
The cooling in the extruded film process is much more efficient than that of blown film. This results in higher production rates with superior optical properties of the product. As the degree of draw and orientation is significantly lower in the cast film process than in the blown film process, the thickness distribution in cross direction is more uniform with cast processes. However, thickness measurement solutions of Hammer-IMS, connected in closed-loop, control the extrusion process to achieve and maintain film thickness variations between 1.5 and 3%.
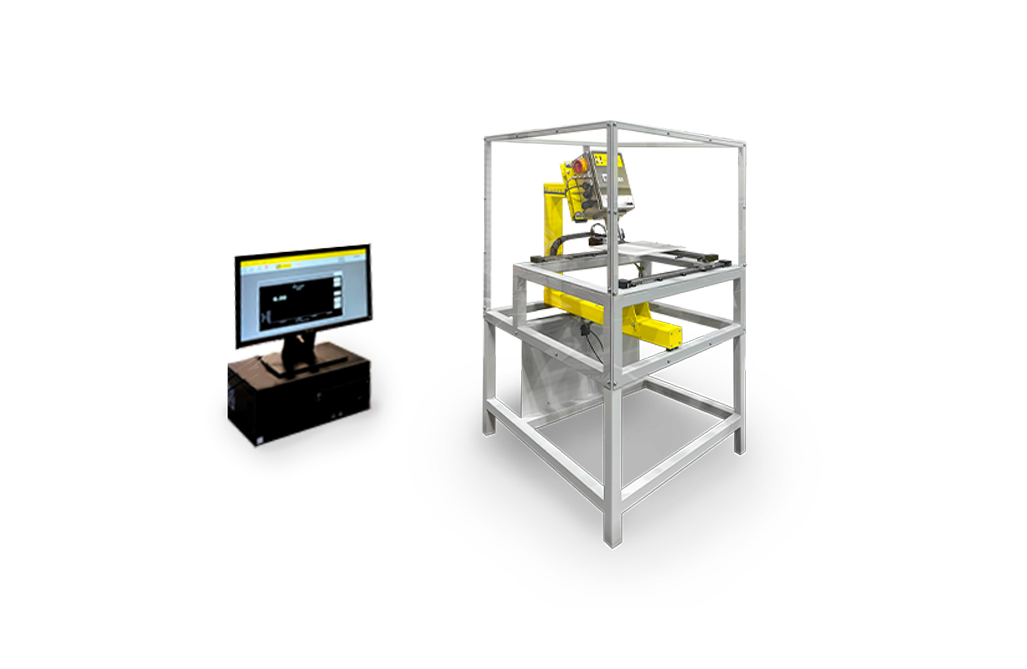
To support high-width production, plastic cast film manufacturers can decide on the frame length of the Marveloc-CURTAIN solution as well as the number of integrated measuring units. The traveling sensors ensure maximum coverage in cross-machine direction. That is the perfect strategy to detect local deviations, which generally correspond to individual screwing bolts of the extrusion die. Thickness measurement in flat film extrusion lines ensures high film quality and reduces the consumption of raw materials.
The M-Ray based measuring solutions of Hammer-IMS offer lower total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to conventional nuclear and radioactive measuring technologies. This is good news for manufacturers with the ambition to equip their production lines with faster and more accurate quality control.
Hammer-IMS measuring system positioned in plastics extrusion line
The M-Ray based measuring systems of Hammer-IMS can be easily placed in a plastics extrusion line on the production floor. Typically, they are located between the cooling rollers and the cutter.
Products for this industry
Edge-Vision-4.0-CURTAIN-O featuring 4k multi-cam
Surface inspection solution for detection of anomalies and defects

Marveloc-CURTAIN-O featuring M-Rays
Machine for thickness measurement of flat materials

Marveloc-CURTAIN-C featuring M-Rays
Machine for thickness measurement of flat materials
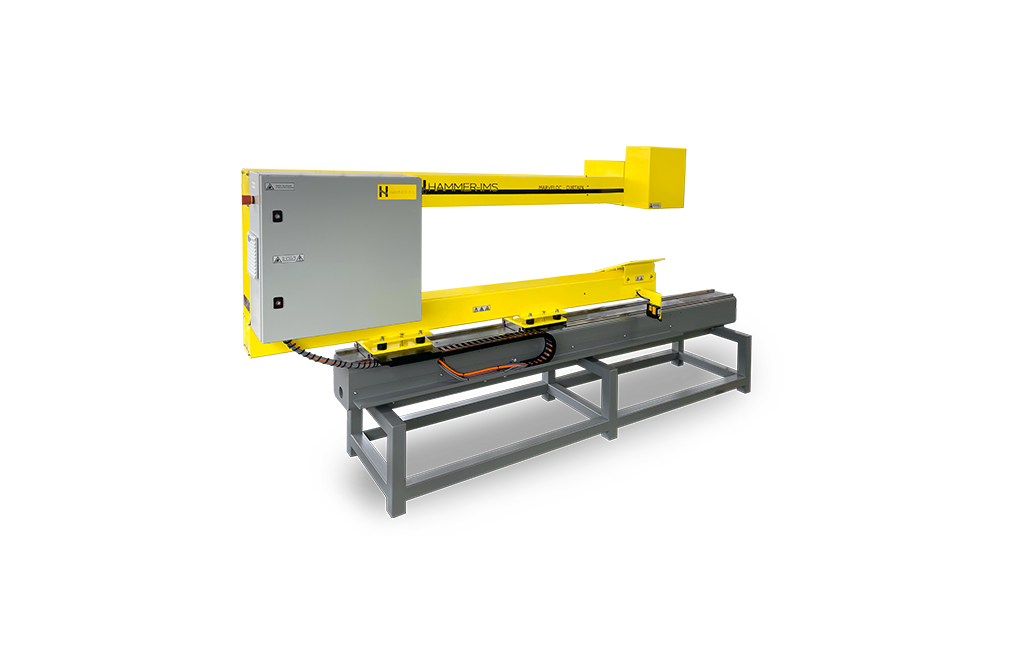
M-Ray OEM Module featuring M-Rays
For OEM projects on thickness measuring by machine builders and sensor integrators

Marveloc-CHARIOT-Capacitive featuring C-Rays
Machine for thickness measurement of flat materials

Marveloc-CHARIOT-Laser featuring L-Rays
Machine for thickness measurement of flat materials

Connectivity 3.0
Industrial software to connect to PLC's and various information sources
Lab devices featuring Miscellaneous technologies
Lab devices, custom or off-the-shelf